Intrauterine Insemination (IUI)
(Artificial Insemination)
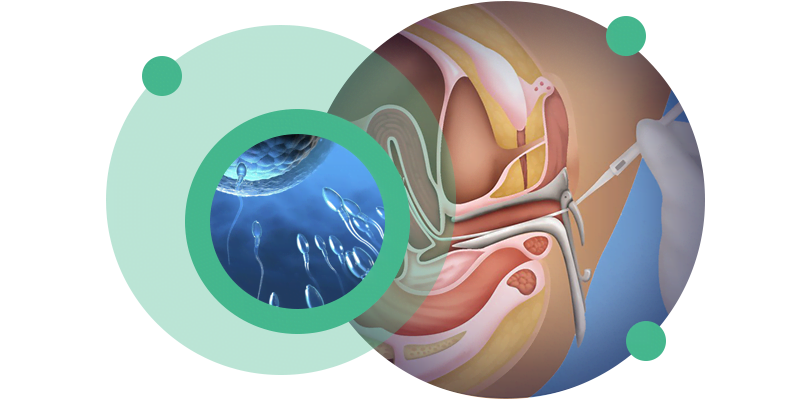
Intrauterine insemination or artificial insemination is a low-complexity, painless medically assisted reproduction treatment that involves placing carefully processed semen (in order to select the best sperm) directly into the woman’s uterus, increasing the chances of successful fertilization. Insemination follows a personalized clinical protocol and does not involve invasive procedures.
About Intrauterine Insemination (IUI)
Intrauterine insemination, commonly known as artificial insemination, is a low-complexity, painless medically assisted reproduction treatment in which carefully selected sperm (after collection processes, washing with appropriate means and selection of the most capable sperm) are placed directly into the woman’s uterus, close to the time of ovulation.
The technique associated with intrauterine insemination or artificial insemination consists of preparing the sperm outside the woman’s body in order to obtain a selection/sample of greater concentration and better quality.
Then, using a thin, flexible catheter, this sample is inserted directly into the woman’s uterus, thereby increasing the likelihood of conception.
Thus, in situations that we can consider in a generic way, in which the monthly probability of pregnancy occurring is reduced in relation to normal, which is 20/25% per month, in couples with this reduction in fertility or subfertility it is possible to prepare sperm in the laboratory, replacing the entire natural selection process that was carried out in the cervix.
The process of sperm selection for insemination begins by placing the sperm in a laboratory centrifuge, along with media with different densities, creating different layers through which the sperm must pass. Only sperm with normal morphology and mobility will be able to overcome the obstacles created by the density gradients.
After this initial centrifugation and selection, the sperm undergo two more centrifugations with washing media. The final step involves the addition of a specific culture medium that will provide energy sources to the sperm, enhancing their mobility and fertilizing capacity.
After this process, sperm are obtained in adequate concentration and quality and are introduced via catheter into the woman’s uterus. This increases the probability of conception by increasing the concentration of gametes in greater quantity and of better quality in the site suitable for fertilization.
Intrauterine insemination can be performed using sperm from the male partner (intraconjugal) or using donor sperm:
Intrauterine insemination with partner’s semen
To perform intramarital IUI, the male partner must collect ejaculate, which will then be processed using appropriate means of washing. After processing, the partner’s sperm will be placed in the upper part of the uterus using a thin, flexible catheter.
Intrauterine insemination with donor sperm
IUI with donor sperm involves the use of cryopreserved, donated sperm. The selected donor sample is thawed and processed for later placement, using a thin, flexible catheter, inside the woman’s uterus.
Donor selection follows strict criteria to ensure the best quality sperm and to minimize the risk of transmitting infections and hereditary diseases. CETI only collaborates with registered and licensed sperm banks.
Natural cycle
IUI using the natural cycle is a viable alternative when the woman is up to 38 years old and her ovarian reserve and ovulation meet the necessary conditions for this purpose. In this situation, there is no need to use drugs as an artificial form of ovarian stimulation. The natural cycle is monitored using ultrasounds to detect the exact moment of ovulation, so that insemination is performed in a short time interval and with high precision.
stimulated cycle
In stimulated cycles, the woman takes ovulation-inducing medications. The development of the follicles is monitored by performing periodic ultrasound scans. When the follicle reaches the appropriate level, an injection is administered to help release the oocyte. Most intrauterine inseminations are performed within 24 to 48 hours.
Intrauterine insemination is considered a first-line treatment and is indicated in situations of:
- Diagnosis of infertility due to immunological or unexplained causes, male infertility (decreased quantity or mobility of sperm), female infertility due to ovulatory or cervical causes (prevention of good sperm preparation), minimal endometriosis and anomalies of the cervix;
- Woman without a partner, using donor sperm;
- Female couple using donor sperm.
Intrauterine insemination or artificial insemination consists of several stages, namely:
- Triggering of the ovarian stimulation process using medication, with a view to developing one or two ovarian follicles with controlled dimensions and maturation levels. This process can be initiated on the 2nd or 3rd day of the menstrual cycle and its progress monitored using transvaginal ultrasound. In certain situations, intrauterine insemination can be performed in a natural cycle, without the use of medication.
- Collection of an ejaculate sample and assessment of its quality (similar to a spermogram) on the day of insemination. If a sperm donor is used, the donor is selected taking into account the blood type and physical characteristics of the recipients. All donors used at CETI undergo rigorous screening tests for infectious and hereditary diseases.
- Laboratory processing of the semen sample to obtain a concentrated and carefully selected solution of sperm. This processing involves several washes of the sample in order to eliminate less capable sperm, as well as other cells and components present in the ejaculate.
- Introduction of the laboratory-processed sample, using a flexible catheter, into the upper part of the uterine cavity. Insemination should occur close to the time of ovulation, in order to increase the probability of fertilization.
- Pregnancy test (Beta HCG) 15 days after insemination treatment.






Frequently Asked Questions
With the start of treatment, marked by the woman’s menstrual cycle, ovarian stimulation begins, which lasts approximately 10 days. When the follicle reaches the appropriate size, ovulation is induced and insemination is scheduled so that the introduction of sperm into the patient’s uterus occurs hours before ovulation, usually 24 to 36 hours after ovulation induction. In total, the entire process takes approximately 12 days.
Ovarian stimulation depends on the protocol used and the individual response of each woman, but it may take, on average, 8 to 10 days.
Yes, a woman’s age influences the results of Intrauterine Insemination. It is known that a woman’s reproductive potential decreases significantly after the age of 35 and drops sharply after the age of 40.
Intrauterine insemination or artificial insemination is a simple and painless treatment.
Artificial insemination is a very safe treatment as long as it is guided and carried out by a doctor specializing in infertility. In cycles with ovarian stimulation, medical monitoring and ultrasound control are extremely important in order to avoid twin pregnancies.
You will need to go to the clinic for ultrasound monitoring of ovarian stimulation or, if performed in a natural cycle, to monitor the moment of ovulation. This ultrasound monitoring should be done every 2 to 3 days. In the case of intraconjugal insemination, the partner will need to go to the clinic on the day of insemination, in the morning, to collect the sperm.
Ejaculate collection can be performed at home, provided that it is possible for the individual to deliver the sample to the clinic premises 30 to 45 minutes after collection. During transport, the container with the sample should be kept close to the body to avoid large temperature fluctuations. The collection container can be provided by CETI or a urine collection container can be purchased at any pharmacy.
Intrauterine insemination or artificial insemination treatment can be carried out at CETI because it is a medically assisted procreation center approved by the Ministry of Health and the National Council for Medically Assisted Procreation.
It is recommended that you take a pregnancy test 15 days after intrauterine insemination.
You can consult CETI’s price list here .
